Apr 13, 2025

What Causes Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD)?
HFMD is caused by viruses, primarily Coxsackievirus and Enterovirus, and commonly affects young children. It spreads through:
Respiratory droplets (coughing, sneezing, mucus).
Oral-fecal route (contaminated hands, surfaces, or objects).
Outbreaks peak during the rainy season due to cool, humid conditions that aid viral spread. The virus can remain contagious for weeks, even after rashes disappear.
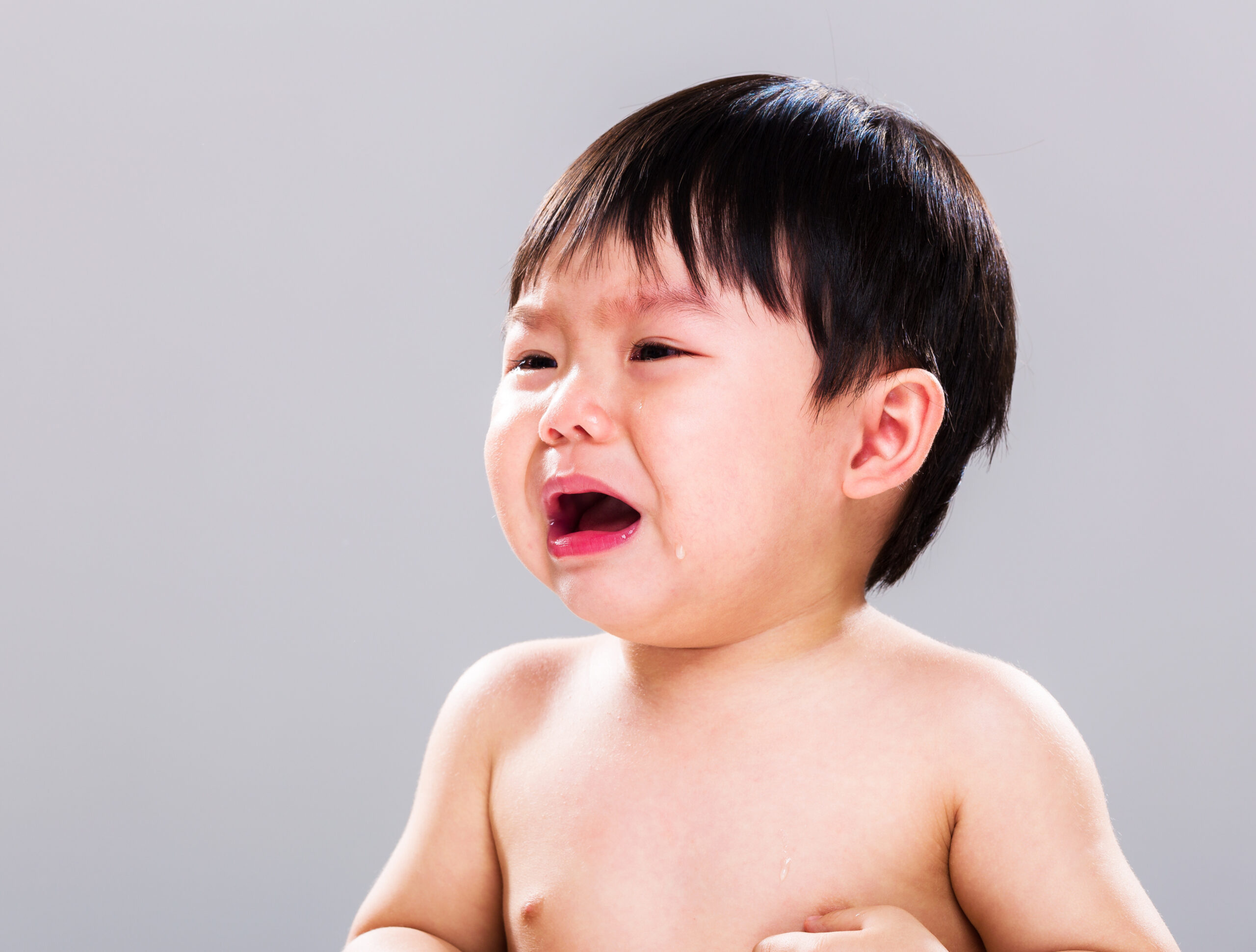
Symptoms of HFMD
After a 3–7 day incubation period, symptoms include:
High fever (38–39°C).
Sore throat, loss of appetite, fatigue.
Painful mouth ulcers.
Red spots or blisters on palms, soles, and occasionally the trunk, arms, or legs.
How to Prevent HFMD
Hand Hygiene:
Wash hands with soap before eating/preparing food and after coughing, sneezing, changing diapers, or using the bathroom.
Teach children proper handwashing techniques.
Disinfection:
Clean toys and high-touch surfaces (e.g., doorknobs) regularly.
Avoid Contamination:
Discourage children from putting hands, toys, or objects in their mouths.
Isolation:
Keep sick children home from daycare/school to prevent spread.
Avoid close contact with infected individuals.
HFMD Vaccination
The EV71 vaccine helps prevent severe HFMD caused by Enterovirus 71, which can lead to life-threatening complications.
Recommended for: Children aged 6 months to 5 years.
Dosage: Two doses, 1 month apart.